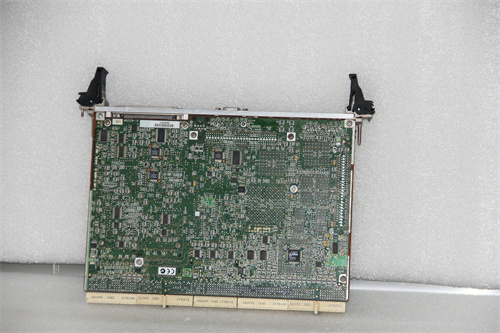
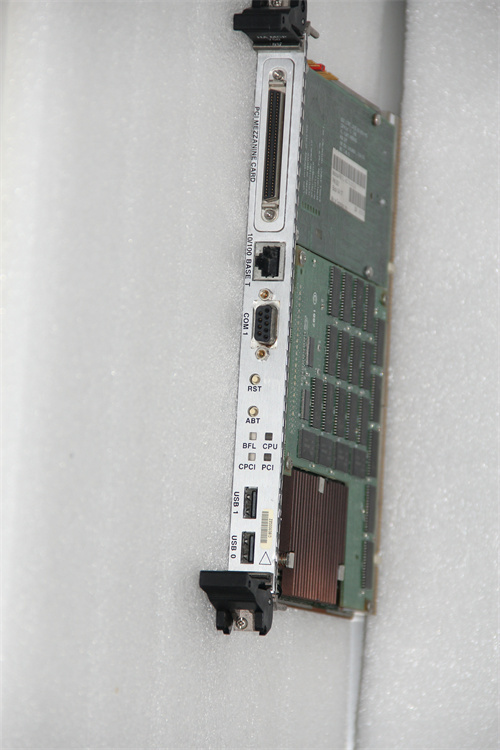
MOTOROLA MCP750 is a product with a wide range of applications in industrial control, data processing and communication systems. The following is a detailed description of the parameters, specifications, size, weight, series, features and functions of the MOTOROLA MCP750:
Parameters and specifications:
Voltage and current: According to some data, its voltage is 24V, and the current range is 100~400A. However, the specific voltage and current parameters may vary for different application environments and configurations.
Performance: The MCP750 provides powerful processing power for a variety of scenarios requiring real-time control and data processing. It is typically based on the PowerPC750 architecture, a 32-bit RISC processor widely used in embedded systems and high-performance computing applications.
Size and weight:
Size: Specific size information may change due to product model and manufacturer updates, it is recommended to consult the latest product manual or official documentation for accurate information.
Weight: The weight is about 2KG.
Series:
The MCP750 is a processor module or controller model in the MOTOROLA (now owned by NXP Semiconductors) family.
Features:
Powerful processing power: suitable for a variety of complex control algorithms and data processing tasks.
Multiple input/output interfaces: Easy to communicate and integrate with other control systems, PLCS, Hmis, sensors and other devices.
Operating system support: Usually supports a variety of embedded operating systems, such as VxWorks, Linux, etc., to provide a flexible environment for application development and operation.
Low power consumption: suitable for industrial applications requiring long running times.
High reliability: optimized and tested to ensure stable operation in industrial environments.
Functions:
Industrial automation: used to control and monitor production lines, robots, conveying systems and other equipment in factories to achieve automated production and process control.
Data acquisition and monitoring system: real-time acquisition and processing of sensor data, monitoring of environmental parameters, such as temperature, humidity, pressure, and equipment operating status.
Mechanical control: Used to control various mechanical equipment, such as motors, actuators, valves, etc., to achieve accurate motion control and position control.